Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
Vectors – Basic Mathematics Form Four
Displacement and Positions of Vectors
The Concept of a Vector Quantity
Explain the concept of a vector quantity

Naming of Vectors:


Equivalent Vectors:



Position Vectors;

Components of position vectors:


Example 2

Solution:

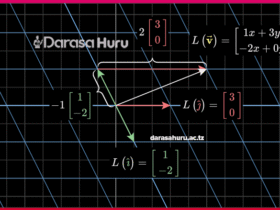
The unit Vectors i and j.


Example 3

Example 4


Magnitude and Direction of a Vector
Magnitude (Modules) of a Vector
Finding the magnitude of given vector.

Using Pythagoras theorem



Unit Vectors:


Direction of a vector:
(a) By Bearings:



Example 7




Alternatively
(b) Direction cosines



Exercise 1

Sum and Difference of Vectors
The Sum of Two or More Vectors
Addition of vectors
(1) Triangle law of vector Addition


(2) The parallelogram law
Find the resultant of vectors u and v in the following figure.

To get the resultant of vectors u and v, you need to complete the parallelogram as shown in the following figure

Note that by parallelogram law of vector addition, commutative property is verified.
Polygon law of vector addition:
Find the resultant of vectors a, b, c and d as shown in the figure below.


Opposite vectors
Two vectors are said to be opposite to each other if they have the same magnitude but different directions



The Difference of Vectors
Normally when subtracting one vector from another the result obtained is the same as that of addition but to the opposite of the other vector.
Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
Consider the following figure

Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar
A Vector by a Scalar
Multiply a vector by a scalar




Application of Vectors
Apply vectors in solving simple problems on velocities, displacements and forces
Vector knowledge is applicable in solving many practical problems as in the following examples.
A student walks 40 m in the direction S 450 E from the dormitory to the parade ground and then he walks 100m due east to his classroom. Find his displacement from dormitory to the classroom.
Solution
Consider the following figure describing the displacement which joins the dormitory D. parade ground P and Classroom C.


Example 14
- Determine the magnitude and direction of their resultant.
- Calculate the magnitude and direction of the opposite of the resultant force.

(b) Let the force opposite to F be Fo, then Fo = -F = – (12, 5) = (-12, -5)
So the magnitude and direction of the force opposite to the resultant force is 13N and S67.40W respectively..
Exercise 2
- The resultant of U + V + W
- The magnitude and direction of the resultant calculated in part (a) above.
2. A boat moves with a velocity of 10km/h upstream against a downstream current of 10km/h. Calculate the velocity of the boat when moving down steam.

Calculate the magnitude and direction of the resultant of the velocities V1=5i + 9j,V2 = 4i + 6j and V3 = 4i – 3j where i and j are unit vectors of magnitude 1m/s in the positive directions of the x and y axis respectively.
Related Posts:
- Topic 1: Coordinate Geometry – Basic Mathematics Form Four
- Topic 2: Area and Perimeter – Basic Mathematics Form Four
- Topic 3: Three Dimensional Figures – Basic Mathematics Form Four
- Topic 5: Trigonometry – Basic Mathematics Form Four
- Basic Mathematics For Form Four Full Notes All Topics
- Topic 7: Matrices and Transformation – Basic Mathematics Form Four
- Topic 8: Linear Programming – Basic Mathematics Form Four




































Leave a Reply