TOPIC 6 GASEOUS EXCHANGE AND RESPIRATION – Biology Notes Form Two New
Gaseous exchange refers to the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the respiratory surface.
Gaseous exchange is the process through which respiratory gaseous are passed through the respiratory surface. Respiratory surface are specialized organs for gaseous exchange. Gaseous exchange takes place through a process of diffusion.
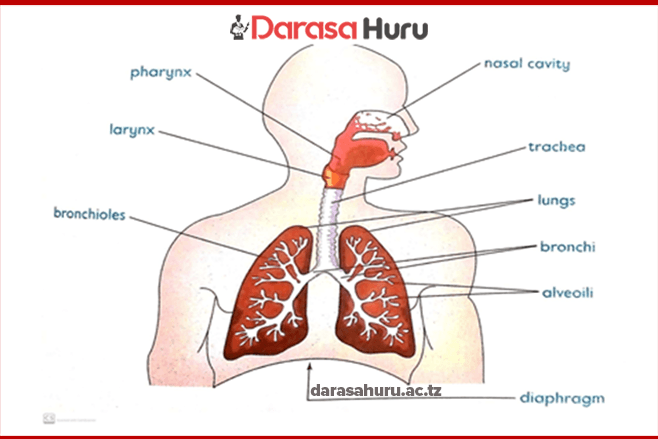
Organs responsible for gaseous exchange in living organisms include the following:
| Organism | Respiratory surface | |
| Amoeba | Cell membrane | |
| Insects | Tracheal system | |
| Spider | Book lung | |
| Fish | Gills | |
| Plants | Leaves, stems , roots | |
| Amphibians | Skin, gills and lungs | |
| Mammals | Lungs | |
| Birds | Lungs | |
| Reptiles | Lungs | |
| Tadpole | External gills | |
| Aquatic mammals | Lungs | |
| Earthworm | Skin |
Features of Respiratory Surface
- They have thin membrane to reduce diffusion distance of gases
- They are moist to dissolve gaseous so that they dissolve and diffuse in solution form
- They are highly branched, folded or flattened in order to increase the surface area for gaseous exchange
- They have a dense network of capillaries that transport gases to and from the gaseous exchange surfaces.
- They are close to efficient transport and exchange easily by the cells
- They are well ventilated so that gaseous passes easily


































Leave a Reply