Topic 4- Pollution – Chemistry Form Four
Pollution can be defined as the introduction by human (or animal) activities, directly or indirectly, of substances or energy into the environment resulting in harmful effects which may endanger human health and harm living resources and ecosystems.
Concept of Pollution
Explain the concept of pollution
- Terrestrial (land) pollution
- Aquatic (water) pollution
- Aerial (air) pollution
Terrestrial Pollution
Explain the concept of terrestrial pollution
Because of the ever-increasing human population, demand for food has increased rapidly. Farmers often use fertilizers to increase crop production and pesticides to get rid of pests, fungi and bacteria that destroy the crops or harm animals. The overuse of such agrochemicals results in the contamination and poisoning of the soil. Other causes of soil pollution from agricultural activities include:
- poor methods of irrigation which causes the leaching of cations down the soil surface;
- manure heaped on land, which may leach down the soil; and
- oil spillages that seep into the soil.

The following are some effects of terrestrial pollution:
- Wastes dumped carelessly can endanger the health of man as well as other organisms. Broken glass, metal and other sharp objects may pierce one‟s skin and introduce disease germs into the body. Empty cans, glass and plastic containers are potential breeding grounds for mosquitoes which spread malaria and other diseases. Rotten organic matter may harbour many disease germs and they also produce noxious smell when they rot. The rotten wastes also attract flies which transmit a number of enteric diseases like dysentery, cholera, diarrhoea, etc.
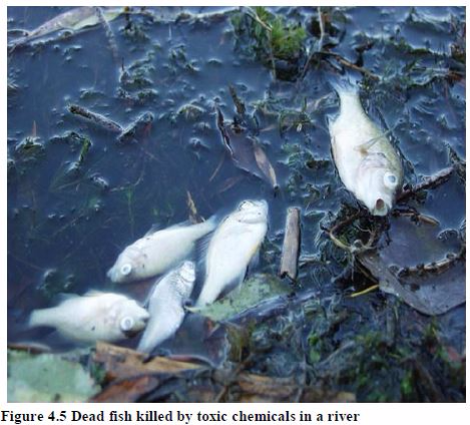
- Land pollution causes chemical contamination to the ecosystem. This occurs when the chemicals in the waste matter poison the soil. Then plants growing on the poisoned soil, animals that eat these plants and even humans are all affected by these chemicals. This process is called biomagnifications and is a serious threat to the ecology. It can lead to the loss of some types of plants and animal life as well as create long-term health problems such as cancer and other deformities in humans. Radiation from nuclear wastes causes healthy problems such as cancers and other deformities.
- Piles of waste in urban areas keep growing due to increase in waste. When this waste is burned it produces a lot of smoke that leads to air pollution.
- Soil erosion (as a form of land pollution) leads to loss of land for agriculture, settlement, forest cover, fodder patches for grazing, etc.
- Land pollution leads to loss of ecosystem and hence directly or indirectly cause change in climatic patterns.
- Deforestation causes imbalance in the rain cycle. A disturbed rain cycle affects a lot of factors such as reduction in the green cover. Plants help absorb excess carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen to the atmosphere. This process helps to balance the atmosphere. Without vegetation cover, excessive accumulation of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causesconcerns like global warming, the greenhouse effect, irregular rainfall, and floods among other imbalances.
- Land pollution damages terrestrial life, especially plants. This greatly affects wildlife and other animal species which are forced to move further away and adapt to new regions or die trying to adjust.
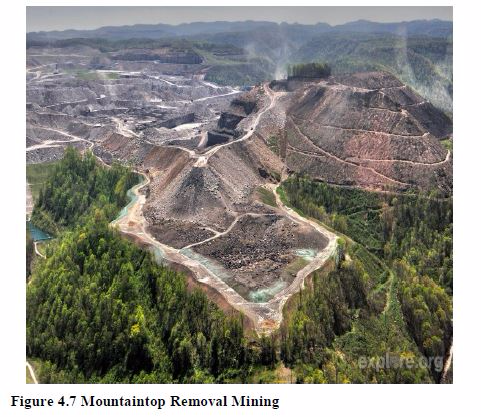
- Heaps of different wastes from mining activities make the environment unsightly and ugly.
- Terrestrial pollution is a big problem in urban areas where waste production outweighs waste disposal. In such areas you find poor and blocked sewage system, effluent from domestic toilets flowing on the streets and roads, and dirty water carelessly poured on the ground. This makes life in urban areas uncomfortable and a mere nuisance.
Suggest different methods of preventing terrestrial pollution
Recycling is the processing of changing used materials into usable raw materials instead of discarding them as wastes altogether. Scrap metals, plastic bottles and glass should be recycled instead of being dumped into the environment. Packaging materials such as plastic bags, beverage and water bottles can be recycled or re-used for packaging or carrying goods.
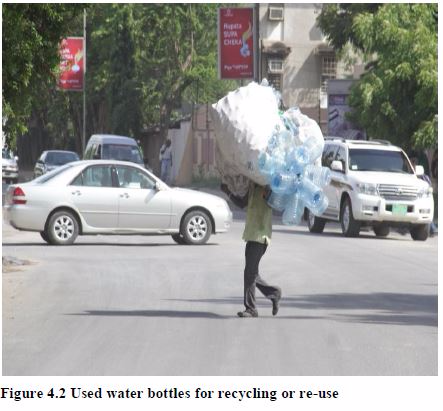

Using biodegradable materials
- biopolymers such as those used in making surgical sutures;
- photodegradable plastics, which break down upon exposure to light: and
- soluble plastics which can be broken down by water
Proper disposal of wastes

Reducing the use of agrochemicals
Making and enacting environmental laws and policies
- discharge and treatment of sewage;
- disposal of lethal nuclear wastes;
- use of agrochemicals in agricultural production;
- use of plastic and related materials;
- disposal of toxic chemicals and solid wastes from industries; and
- careless littering of the environment by irresponsible people.
Creating public awareness
Aquatic Pollution
Explain the concept of aquatic pollution
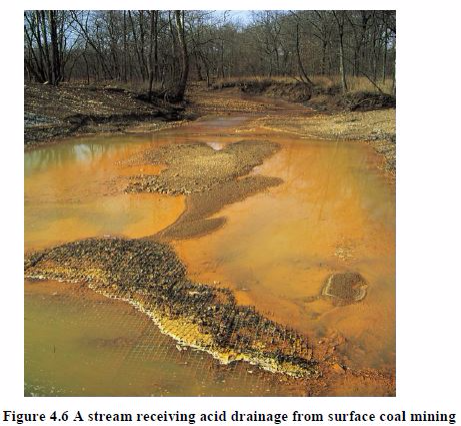
- The mining process exposes heavy metals and sulphur compounds that were previously locked deep in the earth. Rain water leaches these compounds out of the exposed earth, resulting in “acid mine drainage” and heavy metal pollution that can continue long after the mining operations have practically ceased.
- The action of rain water on piles of mining waste (tailings) transfers pollution to freshwater supplies.
- In gold mining, cyanide is intentionally poured on piles of mined rock (a leach heap) to chemically extract the gold from the ore. Some of the cyanide ultimately finds its way into nearby water.
- Huge pools of mining waste slurry (semi-liquid mixture) are often stored behind containment dams. If a dam leaks or bursts, water pollution is likely to take place.
- Mining companies in developing countries sometimes dump mining waste directly into rivers or other water bodies as a method of disposal.

Noise
- Young children and unborn babies are at a higher risk because their body systems are still developing. Exposure to mercury in unborn babies can cause neurological problems such as slower reflexes, learning deficit, delayed or incomplete mental development, autism, and brain damage.
- Mercury can also cause serious nervous system problems in adults. These problems include Parkinson‟s disease, multiple sclerosis, and Alzheimer‟s disease. It can also cause heart disease and damage to the brain.





- Enforcing the regulations and rules that govern maintenance and inspection of commercial ships and other marine vessels that leak oil and fuel into the water.
- Cleaning oil spills as promptly as they occur.
- Converting oil tankers into double-hull ships. A double-hull ship has two complete layers of watertight hull surface. The178outer layer forms the normal hull of the ship. A second inner hull forms a protective barrier to sea water in case the outer hull is damaged and leaks.
- Educating the public how to keep oil out of the environment.
Cleaning up existing and abandoned mines
- Mining companies should clean up abandoned mines which continue to release pollutants to the environment.
- New mines should not be established in areas where they are likely to cause water pollution problems.
- Mining practices which cause water pollution should be banned.
Aerial Pollution


Nitrogen oxides

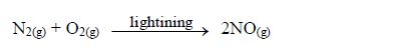
The following are some effects of air pollution.
- CCl3F → •CCl2F + •Cl
- •Cl + O3 → •ClO + O2
- •ClO + O3 → •Cl + 2O2




- the exhaust of new cars are fitted with catalytic converters in which harmful gases are converted to harmless ones;
- manufacturers are looking at ways to make car engines more efficient so that they can use less petrol, and other alternative fuels;
- coal is turned into smokeless fuel for use in homes; and
- scientists are looking at ways to make homes and factories more energy efficient, so that we can burn less fuel, not more.
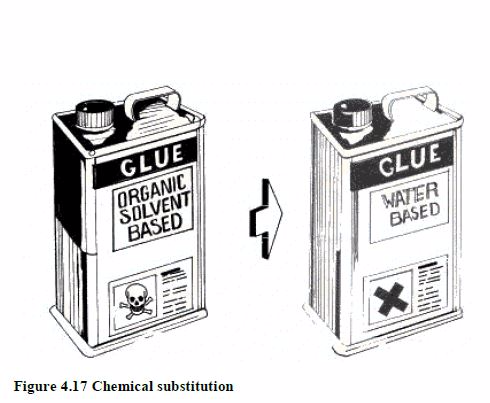
- using water-based paints or glues instead of those that are organic solvent based (figure 4.17);
- using water-detergent solutions instead of solvents; and
- using trichloromethane as a degreasing agent instead of trichloroethylene.

Environmental Conservation
Explain the meaning of environmental conservation
We depend on the environment for our livelihood. It is, therefore, important to conserve the environment for our survival and sustainable development. The following are some of the reasons why environmental conservation is crucial.


- alternative sources of energy;
- methods of preventing and controlling pollution;
- sustainable use of natural resources;
- recycling and reuse of material;
- environmental impact assessment.
- Plant more trees at home and farm fields, school and village forest. Do not cut down tress indiscrimately because doing so leaves the soil bare and vulnerable to soil erosion.
- Always dump litter in areas designated for waste disposal and in litter bins. Do not just throw dirt anywhere and carelessly.
- Do not start fires near forests. Farmers should not prepare their farm fields by burning the vegetation because the fire can spread and destroy trees and nearby forests. Fire also kills important soil microorganisms, thus curtailing soil fertility and productivity.
- Do not harm domestic and wild animals by any means. Be kind to animals and treat them humbly.
- Convey environmental conservation education to all people. Let them know the importance of conserving and living in a clean environment.
- Participate in environmental conservation programmes and tasks. These include World environment Day (June 5, every year) and clear-up exercises in the local area or town.
Global Warming
Explain the global warming in terms of ‘green house’ effect
How the Major “Greenhouse” Gases are Produced
Carbon dioxide is the main greenhouse gas. The gas contributes over 50% of the greenhouse effect. It is because of this reasons that man is struggling to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. The following are some of the man-made sources of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.


- higher or lower agricultural yields;
- melting of arctic ice and snowcaps. This causes landslides, flash floods and glacial lake overflow;
- extinction of some animal and plant species; and
- increase in the range of disease vectors, that is, organisms that cause diseases.
Causes and effects of climate change –> a result of global warming
- Conserving the energy so as to reduce the use of fossil fuels which produce greenhouse gases. Such measures can be taken by using public transport to reduce the number of motor vehicles on the road and using cars that consume a little fuel.
- Minimize the use of deodorants, as they contain CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) that contributes to the ozone depletion, which in turn gives rise to most destructive effects.
- Planting more trees (afforestation) and avoiding cutting down trees (deforestation) carelessly. This is because forests play an important role in absorbing carbon dioxide, thus reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Encourage the use of renewable sources of energy like wind, biomass, solar, and geothermal energy. The use of solar power and biomass should be installed widely. But there are a few obstacles that are delaying the use of these technologies.
- Raise awareness! Educate people about global warming and its disastrous effects. Share various solutions to stop global warming. Make sure you take initiatives to help conserve the environment and encourage others to do the same.
- Countries, including Tanzania, have ratified the international agreements aiming at minimizing the emission of greenhouse gases. One of those agreements is the Kyoto Protocol.
Ozone Layer Destruction
- CCl3F → •CCl2F + •Cl
- •Cl + O3 → •ClO + O2
- •ClO + O3 → •Cl + 2O2
- The most widely used ODS, accounting for over 80% of total stratospheric ozone depletion.
- Used as coolants in refrigerators, freezers and air conditioners in buildings and cars manufactured before 1995.
- Found in industrial solvents, dry-cleaning agents and hospital sterilizers.
- Also used in foam products such as soft-foam padding (e.g. cushions and mattresses) and rigid foam (e.g. home insulation)
- Used in some fire extinguishers, in cases where materials and equipment would be destroyed by water or other fire extinguisher chemicals.
- Used mainly in industry as a solvent in many products and for metal cleaning.
- Used in solvents and some fire extinguishers.
- HCFCs have become major, “transitional” substitutes for CFCs. They are much less harmful to stratospheric ozone than CFCs are. However, HCFCs still cause some ozone destruction and are potent greenhouse gases.
Impact on humans
- Hinders growth and development in larvae.
- Changes behaviour and habits.
- Causes deformities in some species.
- Decreases immunity: Some species have become more vulnerable to diseases and death.
- Retinal damage and blindness in some species.
Suggest methods of protecting the ozone layer
Since their introduction, CFCs have been used as:
- refrigerants in refrigerator and air conditioning units;
- propellants in aerosol cans;
- solvents and blowing agents for insulation foams;
- cleaners in electronic industry;
- fire extinguisher chemicals.



































Leave a Reply