The planet Earth
Download Topic 2: The planet Earth – Geography Notes Form One New Syllabus. The planet Earth is part of a dynamic solar system, interacting with a variety of celestial bodies like asteroids, meteorites, comets, and the moon. The origin of the Earth along its entire system has been researched for hundreds of years.
Various scholars have developed different theories and arguments on how the planet Earth evolved and changed over time. In this lesson you will learn about the Earth.
You will focus on its origin, position in the solar system, shape, and size. The competencies developed will enable you to describe these aspects of the earth and apply, the knowledge to understand and explain the nature and behaviour of phenomena on the earth’s surface.
Origin of the Earth
Activity 1
(a) Use various reliable online sources to search for simulation videos or animations about the origin of the Earth.
(b) Focus your search on the Big Bang theory, Nebula hypothesis, then Inter-stellar dust hypothesis, and prepare a summary of what you have searched.
The Earth is the only known planet in the solar system that supports life. Its surface is made up of land and water bodies. The evolution of the Earth can be traced through various assumption, including both theories and hypotheses, which explain about the origin of the universe.
A number of ideas, principles, and assumptions have been developed by various scholars to trace the origin of the universe from which the planet Earth is found. These assumptions have examined various processes through which the universe, galaxies, stars, and planets were formed, and the changes that are still taking place over time.

Some of the assumptions that explain about the origin of the Earth include the Big Bang theory, Nebula hypothesis, Inter-stellar dust hypothesis, and the Creation theory.
However, various critiques have emerged against these theories, and hypotheses, though they remain important for understanding the evolution of the universe and the planet Earth in particular.
Nebular hypothesis
This is an hypothesis that explains about the origin of the Earth. The hypothesis was proposed by Immanuel Kant in 1755. This hypothesis states that solar system was formed from cold spinning cloud of gases called the Solar nebular.
It resulted from uneven distribution of gases throughout the universe in the Milky Way Galaxy. As the gravitational pull began to condense the gas towards the centre, the speed of the rotation increased. This caused the cloud to flatten, and created an accretion disk.
Matter continued to collect as the force of gravity toward the centre increased. Eventually, the gas warmed from increasing pressure. As the mass further increased, also the gravity increased, and the temperature continued to rise. A ball of hot gas formed in the centre of accretion disk, creating a protostar, also known as the Sun.
Finally, when enough gas gathered in the centre of the protostar, the pressure generated enough heat to fuse the atoms to form a star. Outside the star, matter was forming into clumps of gas, dust and rocks, which created protoplanets that are believed to give rise to the planets.
The theory was modified by Pierre Laplace in 1796. The critiques of the theory were put forward by Pierre Laplace who challenged Immanuel Kant through the following: large amount of heat cannot be generated due to the collision of cold particles of primordial matter as claimed by Kant.
Also, mutual collision of particles cannot generate motion in the primordial matter. Moreover, the random motion of the particles cannot generate circular motion in the primordial matter. On top of that angular velocity of rotary speed of the nebular cannot increase due to increase in size of the nebular as assumed by Kant.

Big Bang theory
This theory was proposed by Lemaitre Georges and Edwin Hubble in the 1920s. The Big Bang theory explains that about 15 billion years ago, a great explosion occurred.
This explosion caused the expansion of universe expand. This explosion is known as the big bang. At the time of this event, all matter and energy in space were contained in one point.
The explosion pushed matter and energy outward expanding in all directions, forming a collection of dust, gas, and stars held together by gravitational attraction. Later, the sun, gas, and dust collided and aggregated into small grains, eventually forming larger bodies called planetesimals (very small planets).
Some of these small planets reached diameters of several hundred kilometres, and later formed the current eight planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) and their satellites.
However, scientists and institutions such as NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) are still investigating to find out if there is existence of other planets in the outer space.
The critique of the theory is that it appears all galaxies emerged at the same time; therefore, they could potentially have at least the same age. However, but this has not been the case. In fact, current astronomical researchers have found that while other galaxies are very old, there are many young galaxies around and far from the Earth.

Inter-Stellar dust hypothesis
In 1943, a Russian scientist Otto Schmidt proposed a theory known as Inter-Stellar dust hypothesis. The theory explains the complex problems of the origin and characteristics of the solar system and the Earth.
According to the Inter-Stellar dust hypothesis, the Sun, during its ‘galactic revolution, captured the dark matter of the universe. The dark matter (Inter-Stellar dusts) of gaseous cloud and dust particles had their own angular momentum.
The dark matter after being attracted by the sun during its ‘galactic revolution’ started revolving around the primitive rotating sun. The intense heat from the sun dispersed the gaseous particles towards the margins of the disk.
Collision among the dust particles started the process of aggregation and accretion around the bigger particles which became the essentials of the future planets. With the passage of time, these embryos captured more and more matter and grew in size to become asteroids.
Furthermore, these asteroids grew in size due to continuous acceleration of nearby matter around them; thus, they became planets. The hypothesis has been criticised that gravitational force of the primitive sun was incapable of capturing dark matter scattered in the universe.
The second critique of this hypothesis is that some astrophysicists believe that meteorites and asteroids were formed from disintegration of planet.
Thus, so they reject the idea that the planets were formed out of meteorites and asteroids.

Activity 2
Search for information on the creation theory from the library or other reliable online sources. Then, prepare points to either oppose or propose the theory in relation to other theories you have studied.
Exercise 1
1. How do you relate the sun, moon, stars, and other objects you see in the sky with the origin of the Earth?
2. Using the theories that you have identified regarding the earth’s origin, complete the provided matrix.

Position of the Earth in the Solar system
Activity 3
Utilise materials readily available in your local area to design a model illustrating the solar system, displaying all the planets and their orbital paths.
According to the origin of the universe, the solar system is found in one arm of the Milky Way galaxy in the universe. The Milky Way is a galaxy with a spiral arm structure and a central bar-shaped region composed of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter. The name “Milky Way” arises from its appearance as a hazy band of light stretching across the night sky.
This band is composed of countless distant stars and other celestial objects. This band is most visible from the Earth in areas with minimal light pollution. It is the galaxy that contains our solar system, where the Earth is found. The Milky Way contains billions of stars. A galaxy is a vast and immense system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity.
These components are held in a specific, organised structure that can take various forms, including spiral, elliptical, or irregular shapes. Galaxies come in a wide range of sizes, with some containing just a few million stars, while others, like the Milky Way, host hundreds of billions of stars. Additionally, galaxies can exist in isolation or be part of larger groups or clusters of galaxies.
The universe is teeming with galaxies and they are the basic building blocks of the cosmic structure. They serve as focal points for astronomical study and are integral to our understanding of the larger cosmos.
Each galaxy, in turn, can be home to its own planetary systems, which may include planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. The Milky Way is just one of billions of galaxies in the universe. It plays a fundamental role in our understanding of the cosmos and it is a subject of extensive study in the fields of astronomy and astrophysics.

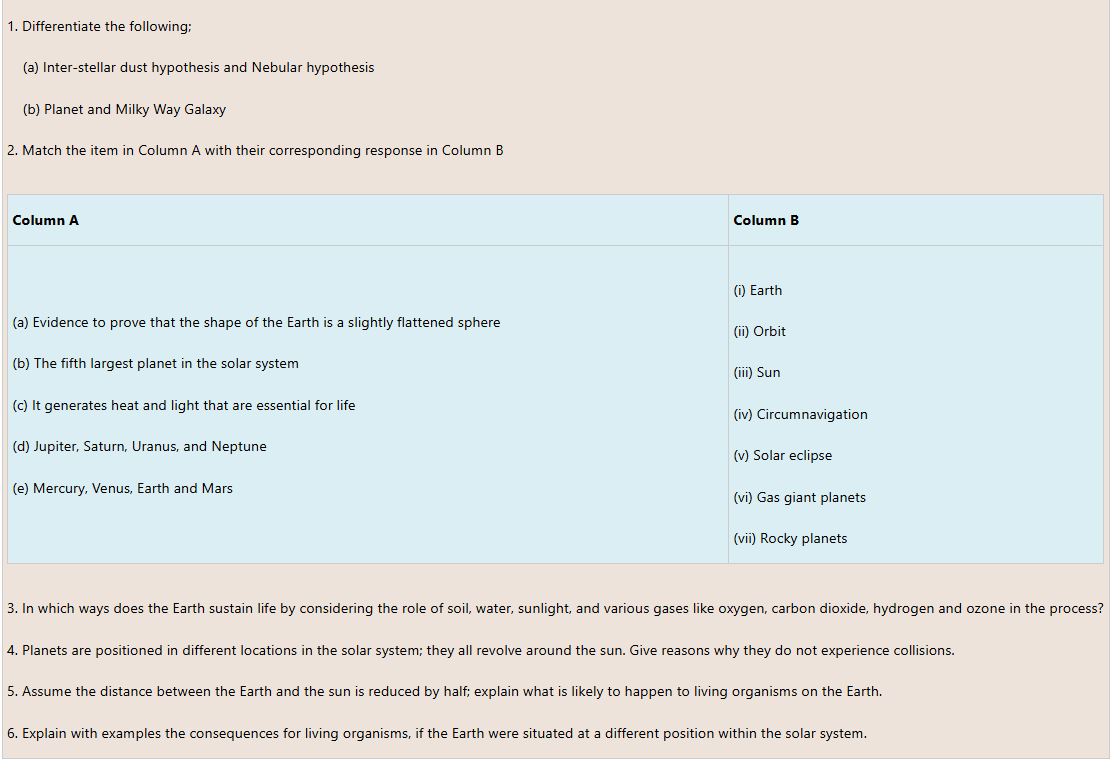
Solar system is composed of a set of different types of planets, moons, asteroids, comets, meteorites, interplanetary dusts and gases. Planets are arranged from the outer gas giants which consist of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune to the rocky inner planets which comprises of Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The inner planets are smaller, hotter, and solid than the outer planets which are large, cold, and gaseous in nature.
The Earth is the third planet in position from the Sun (Figure 2.2). Making life possible is the distinctive features of planet Earth among other planets in the Solar system. The planet Earth is located about 150 million kilometres from the sun. The Earth supports life due to presence of water. Water exists in three states: liquid, solid, and vapour.
It has an atmosphere which contains different gases such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, nitrogen, and ozone gas. All these gases are essentials for life on Earth. Also, the Earth has important nutrients found in the soil, air, and water, which are essential for living things. Furthermore, the position of the Earth in the Solar system makes its temperature suitable for plants and animals.
Due to this, it is evident that the planet Earth is a unique and precious celestial body in the universe. It is the only known celestial body that supports life. Despite this, still the Earth faces numerous challenges, such as climate change, pollution, deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and overconsumption of natural resources, which are associated with unsustainable human exploitation of resources. Increasingly, the challenges are threatening life on the planet.
Exercise 2
1. Explain why the orbit of the Earth around the Sun is not a perfect circle?
2. What is the significance of the distance of the Earth from the Sun?
3. What is the impact of the Earth’s position in the Solar system on weather elements?
Shape and size of the Earth
Activity 4
In a dimly lit room, shine a flashlight towards a spherical object resting on a flat surface like a table. Make sure the flashlight is switched on and is casting a beam of light on the spherical object. Observe the shadow that appears on the wall.
The Earth is the fifth largest planet in the solar system in terms of size and mass. Its shape is like a flattened sphere known as an oblate spheroid (geoid). The flattening of the Earth is very slight as shown by the measurements of the North-south and East-west distances.
The distance through the centre from the North Pole to the South Pole is approximately 12713 kilometres, whereas the distance through the centre of the Earth at the Equator is approximately 12757 kilometres. The circumference of the Earth at the equator is about 40085 kilometres while the polar circumference is 39955

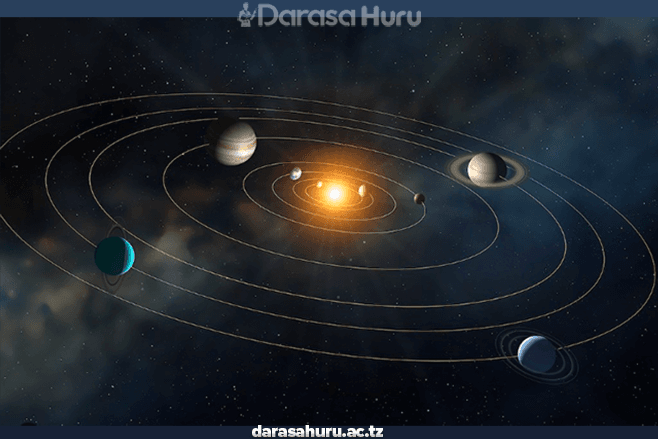
However, the earth’s axis is not upright. It is tilted relative to the plane of its orbit. The axial tilting of the Earth refers to the angle between the earth’s rotational axis and a perpendicular to the plane of its orbit around the Sun.
The earth’s axis of rotation is an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole. This tilting is approximately 23½° angle. The tilt of this axis is responsible for the changing seasons and variations in daylight hours throughout the year. It is significant in shaping the earth’s climate, seasons, and overall environmental conditions.
Activity 5
(a) Use reliable online sources to search for videos or animations of the Earth’s appearance. Study them and comment on the shape of the earth and its horizon.
(b) Relate your observations to the evidence that support the shape of the Earth.
The Earth has an oblate spheroid shape. There are several pieces of evidence to justify the spherical shape of the Earth. Such pieces of evidences include the following:
(i) Sunrise and sunset
The Sun rises and sets at different times in different places of the Earth. People in the East see the sun earlier than those in the West due the spinning of the Earth on its own axis from West to East (Figure 2.4 a). If the Earth was flat, the whole world would have sunrise and sunset at the same time.

(ii) Circumnavigation of the Earth
If you travel from a certain point on the Earth by going in a straight line around it, you will eventually come back to the point of origin. This concept was proved by the first navigator Ferdinand Magellan who sailed around the world from 1519 to 1522. Magellan in his voyage did not encounter any abrupt edge on earth’s surface over which he would fall. This journey around the earth is called circumnavigation of the Earth.

(iii) Aerial photograph of the Earth
Several vertical photographs taken from an airplane or images captured by artificial satellites from great heights show that the Earth is curved (Figure 2.6).

(iv) Ship’s visibility
When watching an arriving ship from the coast, the visibility of the ship, which is far away, starts with the flag, then the mast, and eventually the whole ship is seen as it approaches the coast. When the ship moves away, it gradually disappears starting with the ship, then the mast, and finally the flag. If the Earth was flat, the whole ship would appear or disappear at once (Figure 2.7 a and b).


Lunar eclipse
When light from the Sun is obstructed, a circular shadow is observable. For example, during the eclipse of the moon, the shadow of the Earth on the moon appears spherical

Earth’s curved horizon
The Earth appears to have a curved horizon when viewed from a high cliff, a plane or a high building. The earth’s curved horizon widens as the observer’s altitude increases until it becomes circular.

Exercise 3
1. Give evidence to justify that the Earth is not a flat surface.
2. How does the Earth’s shape affect the occurrence of day and night?
Revision exercise




























Leave a Reply