TOPIC 2: ELECTROMAGNETISM – PHYSICS NOTES FORM FOUR
Magnetic Fields due to a Current-carrying Conductor
How Electric Current Produce a Magnetic Field
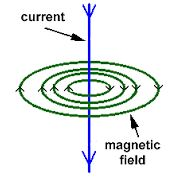
The Pattern of the Magnetic Field Lines around a Straight Conductor
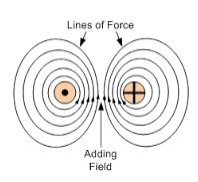
The Direction of Magnetic Field around a Current-Carrying Conductor
- Right-hand Grip Rule
- Maxwell’s cork screw rule
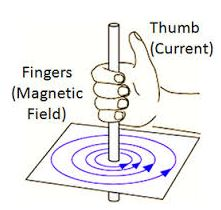
Right-hand Grip Rule

The Presence and Direction of a Force on a Current carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
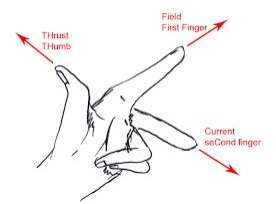
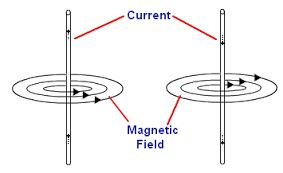
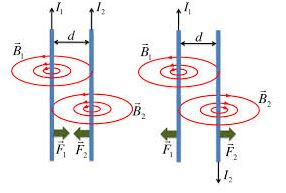
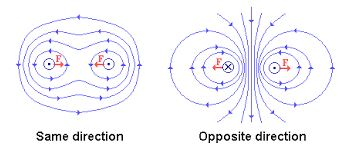
The Direction of Force due to two Current carrying Conductors when the Current Flowing in the Same or Opposite Direction
When the currents are in the opposite directions, the fields between the conductors add up, while they cancel out on the outside. The field between them is stronger than on the outside. The resultant force is toward the outside of each conductor, hence repulsion.
ElectroMagnetic Induction
The Concept of Electromagnetic Induction
The Laws of Electro Magnetic Induction
Lenz’s Law
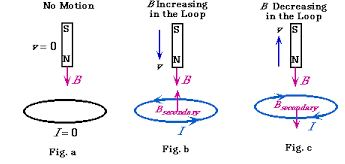
- the strength of the magnetic field.
- the rate of change of the magnetic flux(speed of motion)
- the area of the conductor that is in the magnetic field.
The Concepts of Self and Mutual Induction
The Mode of Action of Induction Coil
Mode of action
- The secondary coil has a large number of turns compared to the primary coil.
- The rapid change in the primary current when it is switched on and off causes a rapid in the magnetic field through the secondary coil.
Applications of the induction coil
- It is used in the ignition system of internal combustion engines.
- It is used to trigger the flash tubes used in cameras and strobe lights.
- It is also used in wireless telegraphy.
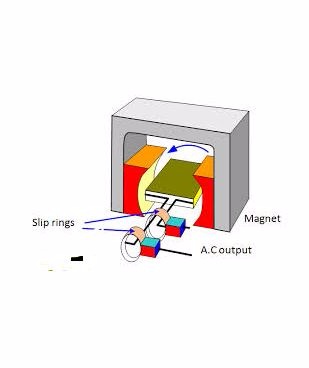
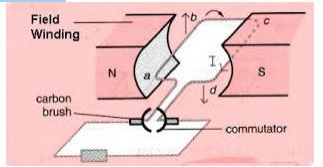
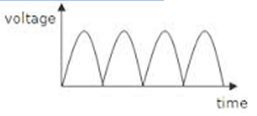
The Mode of Action of a.c and d.c Generator
A.C Generator or alternator





























Leave a Reply