Chapter Six: Business Planning – Business Studies Form Five
Introduction
Failure to plan is a plan to fail. In order to avoid business failure, business owners, managers, and promoters use business plans. Developing a business plan enables the planning of all business activities to be conducted at a certain time.
In this chapter, you will learn about identification of business opportunities and business plan development. The competences developed will enable you to develop a business plan for a medium-sized business.
Identification of Business Opportunities
Business opportunities consist of attractive avenues in the environment, which provide entrepreneurs with the potential for effective business idea development. A promising opportunity always begins with brilliant business ideas. So, while a business idea is a creative thought or concept, an opportunity is an evaluated and promising idea. It portrays a chance to bring that idea to life and make it a reality.
Identification of appropriate business opportunities is an important aspect to business because it enables the entrepreneurs to identify and focus on what customers are missing. An entrepreneur can identify business ideas by scanning the environment for unsatisfied or unfulfilled needs as well as considering customers’ complaints about existing businesses. Once ideas are effectively evaluated on the bases of market potential, competition, resources, and ability of the entrepreneur to pursue the idea, then ideas graduate to opportunities.
Thus, the process of generating good business idea(s) involve a number of processes such as brainstorming to coming up with a number of initial ideas, screening those business ideas, ranking of those business ideas, and mind-mapping the selected business idea on a business model, like Business Model Canvas (BMC). Figure 6.1 provides a summary of the processes which facilitate generation of business ideas.
The following learning tasks and learning activities guide the process of generating good business idea(s):
Use Table 1 to identify the five most unsatisfied or unfulfilled needs and their corresponding target market, business ideas and opportunities based in your community.
| S/N | Problem/gaps/unsatisfied/unfulfilled needs (business opportunity) | Target/market (who) | Business idea(s) (solution / what can be offered?) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | |||
| 2. | |||
| 3. | |||
| 4. | |||
| 5. |
For each of the five business ideas identified in Task .1 respond to the following questions for every idea.
| S/N | Questions for screening your opportunities or ideas | Insert your response |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Are you convinced that there is a ready market for the product? Do you have some indications? | |
| 2. | What is unique? Can you develop competitive advantages over others? | |
| 3. | Do you have, or can you quickly acquire the Key Success Factor (KSF) for the business? | |
| 4. | Is the idea compatible to legal requirements and moral/ethics? | |
| 5. | Is the market saturated? If yes, think twice. | |
| 6. | Is the idea compatible with community’s values and life style? | |
| 7. | Does it have growth potential? Is the industry declining/stable/growing? | |
| 8. | Can you raise the investment capital required? How? | |
| 9. | What makes you the best person to do this business? |
Use the responses on Task 2 to rank the business ideas from 1 to 5, where 1 represents the lowest or poorest and 5 is the highest or best. Then, select one business idea with the highest score.
| S/N | Criteria | Idea 1 | Idea 2 | Idea 3 | Idea 4 | Idea 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Market availability | |||||
| 2. | Uniqueness | |||||
| 3. | Compatibility with the legal requirements | |||||
| 4. | Compatibility with the community | |||||
| 5. | Your capability (skills, knowledge) | |||||
| 6. | Ability to raise or acquire capital | |||||
| 7. | Growth potential | |||||
| Total scores | ||||||
Mind Mapping the Selected Business Idea on a Business Model Canvas (BMC)
Activity 1
Visit the school library or online sources and review literature on different business models including Business Model Canvas (BMC).
- Use the Business Model Canvas (BMC) components reviewed in Activity 6.1 to mind map the selected business idea with the highest score in Task 6.3.
- Based on your selected idea, write two pages summary responding to the following questions:
- The broad idea – What is the business?
- What is the customer need and how does the product meet this need?
- How is your idea better than that of your competitors, if they exist?
- Who will be your target market – Who are the customers?
- How will you make or offer the product?
- What will be the location of the business?
- How will it make a profit?
- What amount or funding is needed, what for, and what has already been acquired?
- What is the prospect or growth of the idea?
- Why are you the one(s) most appropriate for this business?
Exercise 1
- Explain the link between unmet needs, business opportunities, and business idea
- What are the possible sources of business ideas?
- What are the criteria for screening the business ideas?
- Briefly explain the key components of a Business Model Canvas (BMC)
Skills Lab Activity
Based on your understanding of business idea generation, how can you help the school community to do the same?
Business Plan Development
A business plan is developed using the business opportunity generated from the business ideas. Once an entrepreneur has generated a viable business idea, then, the development of a business plan starts. The business plan document involves the following components: business description, industrial analysis, market assessment, marketing plan, operations plan, management and organisational plan, and financial plan as shown in Figure 6.2.
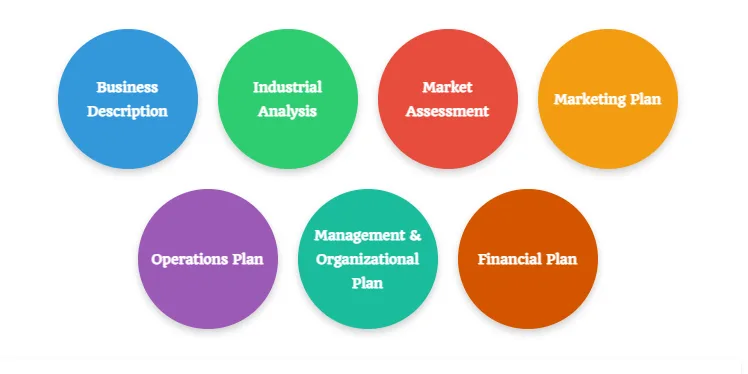
Business description entails the basic information about the business including the product (s) offered, owner(s), and location of the business. Market assessment provides information on the extent of product demand in the market as well as the industrial analysis. Market assessment mainly focuses on determining strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the market. Based on the market status information obtained during the market assessment, an entrepreneur may decide on the marketing plan and strategies to be used in generating more customers (markets) for the product(s).
The operation plan focuses on how the product (s) will be produced and delivered to the customers. The organisational plan provides the human resources needed and their roles for the implementation of the business. Finally, the financial plan reflects cost implications of all items from all sections of the business plan in order to inform the prospective financial performance of the business.
The following learning tasks will expand your knowledge of how to develop a business plan using the selected business idea:
Use Table 4 to describe the business based on the business idea selected in Task 6.3.
| S/N | Items | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Proposed business name | |
| 2. | Business location | |
| 3. | Owner’s details | |
| 4. | Mission | |
| 5. | Vision | |
| 6. | Core values | |
| 7. | Products | |
| 8. | Legal structure of the business |
Use Table 5 to list possible strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges or threats of your proposed medium-sized business.
| S/N | Items | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Strengths | |
| 2. | Weaknesses | |
| 3. | Opportunities | |
| 4. | Challenges or threats |
1. Use Table 6 to list the Key Success Factors (KSF) in line with your business idea.
| S/N | List of Key Success Factors (KSFs) |
|---|---|
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. | |
| 4. | |
| 5. |
2. Use Table 7 to list the types of customers you are likely to serve and their profiles or characteristics.
| S/N | Customer type | Profile or characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Customer A | |
| 2. | Customer B | |
| 3. | Customer C |
3. Use Table 8 to describe the profile of your competitors.
| S/N | Competitor | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Competitor A | ||
| 2. | Competitor B | ||
| 3. | Competitor C |
4. Project your sales using Table 9 for at least three years. Remember to note down all the assumptions used in projecting the sales. The forecast can be both in quantity and value (TShs). The estimates of Year 2 can base on Year 1 likewise Year 3 may depend on Year 2.
| S/N | Customer group | Year 1 (Qty/TShs) | Year 2 (Qty/TShs) | Year 3 (Qty/TShs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Customer A | |||
| 2. | Customer B | |||
| 3. | Customer C |
Marketing Plan
1. Use Table 10 to state at least three marketing objectives that you are likely to achieve over a period of three years. The objectives may be in terms of profitability, market share, awareness, price leadership, brand equity and many others. Remember, they should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Time bound (SMART).
| S/N | Marketing objective (for example increase market share by 5% in the year 20XX) |
|---|---|
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. |
2. Use Table 11 to identify your marketing strategies in the upcoming three years in line with your proposed medium-sized business venture.
| S/N | Marketing mix variable | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Product strategies | |||
| 2. | Pricing strategies | |||
| 3. | Promotion strategies | |||
| 4. | Distribution strategies |
3. Use Table 12 to state the amount of money you will use in implementing the marketing strategies proposed in question 2.
| S/N | Strategies | Year 1 (TShs) | Year 2 (TShs) | Year 3 (TShs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ||||
| 2. | ||||
| 3. | ||||
| 4. | ||||
| Total marketing expenditure | ||||
Operations Plan
1. Use Table 13 to respond to the following questions:
| S/N | Questions | Responses |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | What are the justifications for business location suggested (example: proximity to customers, or and raw materials)? | |
| 2. | What size of land is required to start and operate the medium-sized business? Is it expected to be purchased or rented? | |
| 3. | What kind and number of premises do you need? | |
| 4. | Are there special facilities or equipment needed? State them. | |
| 5. | Who are the suppliers of the resources needed? State them. | |
| 6. | What are the labour requirements to produce or deliver products? | |
| 7. | What are the product delivery plans in place? |
2. Use Table 14 to list inputs needed to produce or deliver the services at the start of the business.
| S/N | Inputs | Amount (TShs) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Raw materials | |
| 2. | Consumables (example filters, and bags) | |
| 3. | Others |
3. Use Table 15 to establish the production plan (for businesses related to the manufacturing of physical goods).
| S/N | Products | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Product A | |||
| 2. | Product B | |||
| 3. | Product C |
Management and Organisational Plan
Present the organisation structure of the proposed business. In each position identified in the organisation structure provide the details as indicated in Table 6.16.
| S/N | Position | Duties/responsibilities | Qualifications | Salary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ||||
| 2. | ||||
| 3. | ||||
| 4. |
Financial Plan
A financial plan provides details of the roadmap through which the business will undertake its financial activities to realize its objectives. It serves as an important component of a comprehensive business plan providing a clear projection of the business’s financial performance over a specific period of time. The following are the sample components that may be used to provide details in the financial plan:
1. Use Table 17 to estimate the initial and working capital requirements to start your medium-sized business.
| S/N | Item/particulars | Amount (TShs) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Machines | |
| 2. | Land acquisition | |
| 3. | Motor vehicle(s) | |
| 4. | Working Capital (Operational expenses for at least the first three (3) months) | |
| Total funding needed | ||
2. Use Table 18 to establish the possible sources of funds.
| S/N | Sources of funds | Amount (TShs) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Own savings | |
| 2. | Family loan | |
| 3. | Family investment partner(s) | |
| 4. | Micro-credit scheme | |
| 5. | Bank loan | |
| 6. | Equity partner | |
| 7. | Venture capital company | |
| 8. | Other | |
| Total expected funding | ||
3. Use Table 19 to list all the key assumptions for forecasting the income to be generated.
| S/N | Assumptions |
|---|---|
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. | |
| 4. | |
| 5. |
Financial Performance
1. Use Table 20 to project the profit and loss of the business.
| Particulars | (TShs) | (TShs) |
|---|---|---|
| Sales/income | XX | |
| Cost of sales: | ||
| Opening inventory | XX | |
| Add: Purchases | XX | |
| Less: Closing inventory | (XX) | |
| Cost of goods sold | (XX) | |
| Gross profit | XX | |
| Less: Other expenses | ||
| Rent | XX | |
| Electricity | XX | |
| Business rates | XX | |
| Depreciation expense | XX | |
| Irrecoverable receivable expenses | XX | |
| Total expenses | XX | |
| Net profit/Net loss for the year | XX | |
2. Use Table 21 to project the financial strengths of the business.
| Particulars | (TShs) | (TShs) |
|---|---|---|
| Assets | ||
| Non-current assets | ||
| Premises | XX | |
| Plant & equipment | XX | |
| Vehicles | XX | |
| Furniture & fittings | XX | |
| Land | XX | |
| Total non-current assets (A) | XXX | |
| Current assets | ||
| Inventory | XX | |
| Receivables | XX | |
| Bank | XX | |
| Cash | XX | |
| Prepayments | XX | |
| Total current assets (B) | XXX | |
| Total Assets (A + B) | XXX | |
| Capital and liabilities | ||
| Capital | ||
| Capital at start | XX | |
| Add: Profit for the year | XX | |
| Less: Drawings | XX | |
| Total capital at close (C) | XXX | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Non-current liabilities | ||
| Loan from XX | XX | |
| Other non-current liabilities | XX | |
| Total non-current liabilities (D) | XXX | |
| Current liabilities | ||
| Payables | XX | |
| Accruals | XX | |
| Other current liabilities | XX | |
| Total current liabilities (E) | XXX | |
| Total liabilities (D + E) = F | XXX | |
| Total capital and liabilities (C + F) | XXX | |
Task 13
Prepare a comprehensive business plan for a business of your choice.
Exercise 2
- What constitutes an operations plan as part of the business plan?
- Identify and discuss the components of a well-packaged business plan.
- What would you consider important in developing a management and organisation plan for a business?
Project Work
You have noted that the majority of the medium-sized business owners lack skills for writing a business plan. Prepare a business plan training checklist for the business owners.
Chapter Summary
- In ranking the business ideas, it is important to consider several factors including market availability, uniqueness of the product or idea, compatibility of the idea with legal requirements and promoter’s capability to manage the proposed business and ability to raise the required capital for the business.
- In mind mapping a business idea, it is important to use appropriate business model such as Business Model Canvas (BMC).
- The key components in developing the business plan are business description, industrial analysis, market assessment, marketing plan, operations plan, management and organisation plan and financial plan.
- The business description component includes the business name, owners’ details, mission and vision, products, as well as legal status.
- Industrial analysis focuses on the internal and external aspects of the proposed business. The internal aspects are the strengths and weaknesses whereas the external ones include the opportunities and threats or challenges.
- Market assessment evaluates the key success factors, profile of customers and competitors.
- A marketing plan includes the marketing objectives, product description, pricing, promotion, distribution, strategies and predicted expenditure.
- An operations plan contains the basic information on the rationale of business location, size of the area required, premises, facilities, and equipment needed. In addition, it includes raw materials, labour requirements, utilities, production and delivery plans.
- A management and organisation plan presents the organisation structure, qualifications of the various categories of staff, job description, and salaries or remunerations of the key positions.
- A financial plan outlines the funds needed, sources of funds and expected financial performance by providing details on the income statement, statement of financial position, and cashflow statement.
Revision Exercise
- What are the possible sources of business ideas?
- Describe the criteria used in ranking business ideas.
- What are the key aspects to consider when screening business ideas?
- Being an expert in business planning, you have been invited by Tanzania Chamber of Commerce, Industry and Agriculture (TCCIA) to address owners of Medium Enterprises (MEs) who argued against developing a business plan. They stated that developing a business plan is a tedious exercise that is time consuming and wastage of resources. Prepare a presentation that explains how you would address them on why they should embark on developing a business plan.
- What are the key steps in the development of the business plan document?
- Kimatare Enterprise Ltd. has embarked on producing bottled water. The business is expected to be marketed widely in Dar es Salaam and Coast Regions. The Company intends to target low and middle-income earners. The bottled water products are in different Stock Keeping Units (SKUs) including: 500ml, 1,000ml, 1,500ml, 1,700ml and 2,000ml. The distribution strategy will involve strategic agents (operating on exclusivity rights), wholesalers, and retailers. The targeted retailers include supermarkets, petrol station food marts, kiosks, hotels and restaurants. The owner plans to launch the business in January next year, however before the official launch, management has approached you and would like to have more details on how the Business Model Canvas (BMC) can help in conceptualising their business. Prepare and present the BMC based on the information given and your experience.
- Based on your experience in business planning processes, describe the following:
- The relationship between marketing plan and market assessment.
- The relationship between marketing plan and operations plan.
- The relationship between marketing plan and financial plan.
- With examples, briefly describe the key components of a marketing plan section.
- What would you include in developing a financial plan for your medium-sized business?
Conducting a Project in Business Studies
Select an area of your interest related to Business Studies, then design and conduct a project.




























Leave a Reply