Viruses and Major Groups of Living Things
There are many species of living organisms in the world. These organisms are placed in groups based on their common or shared characteristics. Each group has its own features that make it distinct from others.
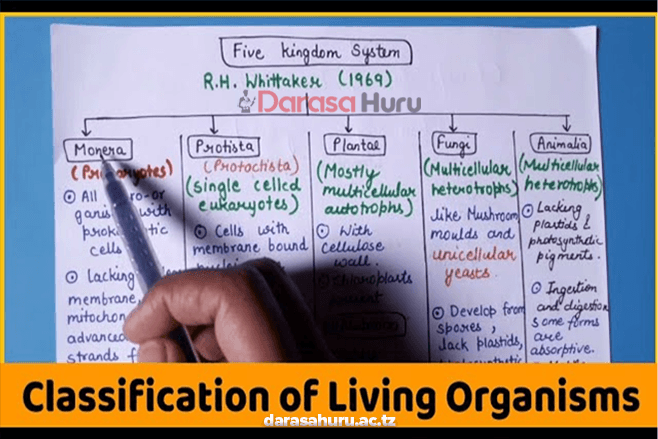
In this lesson, you will learn about viruses and five kingdoms of organisms, namely, Monera, Protoctista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia. The competencies developed will enable you to distinguish members of these groups, understand their interrelationships and explore their importance to human beings and other organisms.
Viruses
Task 1
From the library and reliable internet sources, search for information about the characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of viruses.
A virus is an extremely small fragment of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat. It is smaller than a living cell. A virus is not a cell. Examples of viruses are shown in Figure below
Characteristics of viruses
(a) They do not have a nucleus, cytoplasm, or cell organelle.
(b) They have a simple structure consisting of a small piece of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid. Some viruses have viral envelopes. These are membranes enclosing the capsids. The envelopes are made up of proteins from the host cell.
(c) They cannot reproduce on their own. They must attack a host cell and use the materials in that cell to reproduce. This is called obligate parasitism. The ability of a virus to reproduce inside the cell and crystallize in the absence of a living host places them between living and non-living things. Figure 5.2 shows how some viruses attacking and reproducing inside the host cell.

(d) When outside a host cell, they show no symptoms of life (do not grow, feed, excrete, or respire). They exist in a dormant state.
(e) They are host-specific. This means that a certain type of virus attacks only a specific host. For example, the rabies virus affects only mammals and HIV attacks only certain types of white blood cells in human beings.
(f) Most viruses are infectious: This means they can cause diseases to their hosts.
The structure of viruses
Viruses are composed of strands of genetic material (DNA or RNA) which forms the core. The core is enclosed by a protein coat called capsid as in bacteriophage. DNA or RNA are of various shapes and sizes according to the type of the virus. Examples of the structures of viruses are shown in Figure
Advantages of viruses
(a) Viruses are important in the study of cell and molecular Biology. They are used by scientists to manipulate and investigate the functions of cells.
(b) Some viruses are used to make vaccines. For example, the first vaccine against smallpox was a small dose of the virus that causes cowpox, which is a mild infection. On recovering from cowpox, the body developed antibodies that could resist both cowpox and smallpox.
(c) Bacteriophages are viruses that attack bacteria. They help in controlling bacterial infections and diseases.
(d) Some viruses are used in biological control to eradicate pests, such as insects. This is due to their characteristics of being host specific and infectious.

Disadvantages of viruses
(a) Most viruses are pathogenic. They cause infections and diseases, such as tobacco mosaic disease, tomato spotted wilt disease, cassava mosaic disease, rabies, chickenpox, COVID-19, polio, and AIDS. Pathogenic viruses can reproduce very fast, leading to large-scale epidemics.
(b) Viruses can alter themselves often, and thus become difficult to cure viral infections. For example, there are many different types of viruses that can cause common cold and influenza.

Exercise 1
1. Why are viruses regarded as non-living things?
2. Explain why some viruses are used in agriculture to fight against pests and disease vectors.
3. Viruses can be regarded as a threat to human health. Explain.
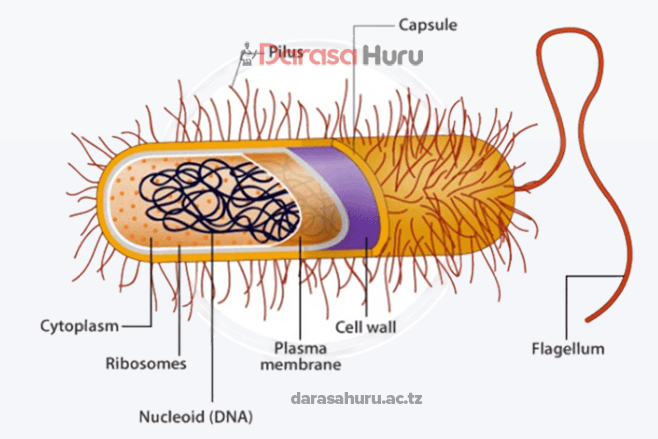
Kingdom Monera
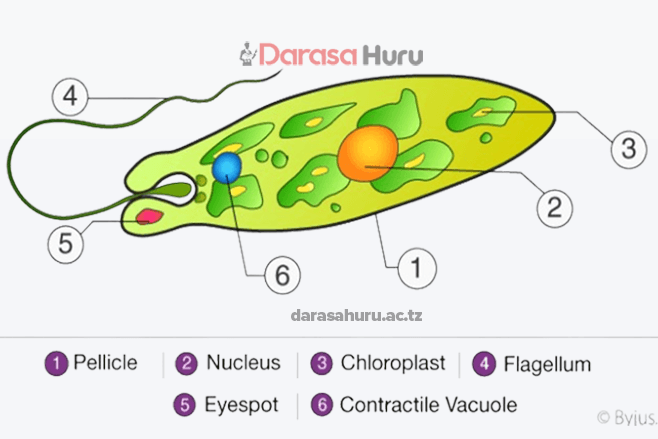
Kingdom Protoctista
Kingdom Fungi
Kingdom Plantae
Kingdom Animalia
Chapter summary
1. A virus is an extremely small microscopic agent. It is not a cell.
2. Kingdom Monera consists of bacteria and blue-green algae. Bacteria can be pathogenic or non-pathogenic.
3. Kingdom Protoctista includes Amoeba sp., Plasmodium sp., Euglena sp., Paramecium sp., and Trypanosoma sp.
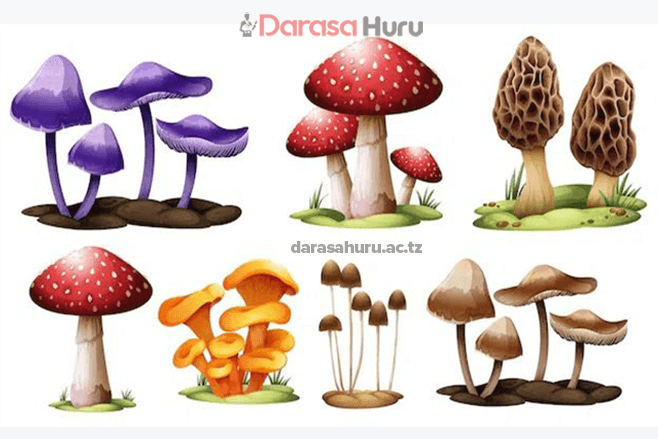
4. The main phyla of kingdom Fungi are: Ascomycota, for example baker’s yeast; Zygomycota, for example black bread mould and mucor; and Basidiomycota, for example mushrooms, and toadstools.
5. The main divisions of kingdom Plantae are: division Bryophyta, division Filicinophyta or Pteridophyta, division Coniferophyta, and division Angiospermophyta.
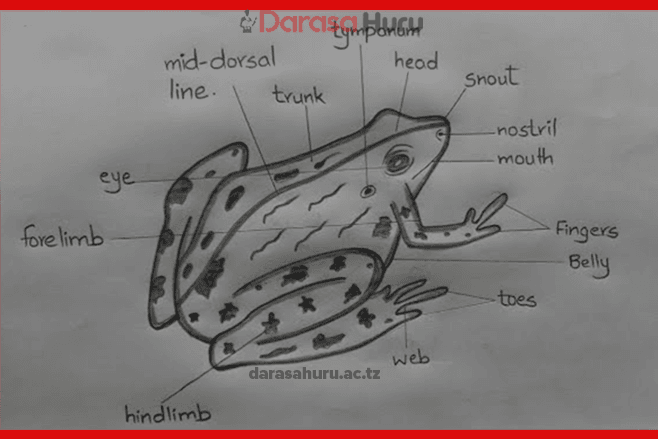
6. Vertebrates are animals that possess vertebral column. Examples of such animals include fish, frog, and human being. Invertebrates are animals that do not possess the vertebral column. Examples of such animals include worms and grasshoppers.
7. Features that differentiate members of kingdom Animalia from other organisms include ability to move from one place to another and possession of a well-developed nervous system that helps them in detecting changes in their surroundings.
8. Phyla of the kingdom Animalia include Platyhelminthes (flatworms), Nematoda (round worm), Annelida (segmented worms), Arthropoda (animals with jointed appendages), and Chordata (animals possessing supporting skeletal structure called vertebral column).
Revision exercise
Choose the correct answer in questions 1- 7.
1. The following are diseases caused by fungi in plants and animals EXCEPT _____.
(a) wheat rust and maize rust
(b) candidiasis
(c) influenza
(d) powdery mildew
2. Which of the following is the advantage of bryophytes?
(a) They cause fungal diseases in human beings
(b) They help to retain water in the soil
(c) They reproduced resins
(d) They are good sources of timber
3. One of the following plants is an example of conifers.
(a) Mango tree
(b) Orange tree
(c) Coconut tree
(d) Pine tree
4. Which of the following groups of organisms belong to the same Phylum?
(a) Liver fluke, hook worm, earthworm, and spider
(b) Tapeworm, earth worm, grasshopper and rat
(c) Butterfly, grasshopper, frog, and elephant
(d) Crabs, grasshopper, spider, and centipede
5. Which of the following is among the distinctive features of annelids?
(a) Their bodies have similar body segments
(b) They have a cylindrical, elongated and unsegmented body
(c) They are dorso-ventrally flattened
(d) They have suckers, hooks or both
6. Which of the following is not a distinctive feature of animals?
(a) They depend on other organisms as source of food
(b) Most of animals are capable of locomotion
(c) They have well developed nervous system
(d) They have exoskeleton
7. Which of the following is correctly matched?
(a) Platyhelminthes – segmented worms
(b) Nematoda – round worms
(c) Annelida – jointed appendages
(d) Arthropoda –flatworms
Write “TRUE “for a correct statements and “FALSE” for an incorrect statements in the spaces provided.
8. A virus is an extremely small organism. _______
9. Kingdom Monera includes Amoeba sp. _______
10. Plasmodium sp. is a parasite that causes sleeping sickness. _______
11. Rhizoids are found in moulds and mosses. _______
12. Coniferophyta is one of the divisions of the Kingdom Plantae. _______
13. Explain the effects of the following organisms to humans.
(a) Entamoeba sp.
(b) Plasmodium sp.
(c) Trypanosoma sp.
14. List characteristics of phylum to which Euglena sp. belongs.
15. A bread was put in a moist cupboard. After a few days black thread-like structures which ended up in club-like structure appeared on the bread.
(a) Write the common name of the organism that grew on the bread surface.
(b) Name the kingdom to which the observed organism belongs.
(c) Name the phylum or division in which the observed organism belongs.
(d) Outline the advantages of the members of the kingdom you mentioned in (b) above.
16. What features make cockroach and human being to belong in the same kingdom?
17. Classify each of the following organisms to phylum level; (a) tape worm, (b) housefly and (c) monkey.
18. Mtakuja villagers believe that all insects are dangerous. They decided to kill them by spraying insecticide. As a biologist, convince them that insects are beneficial to their lives.



































Leave a Reply