Kingdom Plantae Classes, Advantages and Disadvantages
Kingdom Plantae is composed of a wide variety of plants. Members of this kingdom vary greatly in size, forms, habitat, means of reproduction, and morphology.
Kingdom Plantae includes; moss, ferns, cone bearing plants, and flowering plants. Plants are found in various habitats, such as on land, in oceans, and in freshwater.
Activity 6
Investigating plant parts
Materials
A variety of plants, hand lens, notebook and pen or pencil
Procedure
1. Collect a variety of plants from the school or home environment.
Caution
Care must be taken when collecting plants, some plants such as milkweed and oleander are poisonous.
2. Examine each of the plant parts using a hand lens. The parts to be examined include roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits. Do all plants have these parts?
3. Group the plants according to their similarities and differences.

General characteristics of members of the kingdom Plantae
(a) They are multicellular and eukaryotic organisms.
(b) They have cell organelles called chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll.
(c) Green plants are photoautotrophs. This means that they manufacture their own food using sunlight through the process of photosynthesis.
(d) Some plants reproduce sexually through flowers or cones while others reproduce asexually by means of spores or vegetative propagation.
(e) Their cells are organised into tissues, organs, and organ systems.
(f) They show limited movement, for example opening and closing of flower petals and growth movements towards stimuli such as light and water.

Distinctive features of members of the kingdom Plantae
(a) They have a cell wall made up of cellulose.
(b) Higher plants have vascular tissues for conduction of water, mineral salts, and manufactured food.
(c) They store food in the form of starch.
Divisions of kingdom Plantae
The kingdom Plantae is divided into four main divisions. These are: division Bryophyta; division Filicinophyta or Pteridophyta; division Coniferophyta; and division Angiospermophyta.
Division Bryophyta
Members of the division Bryophyta are called bryophytes, which are the most primitive plants. They are found in wet and shaded environments, such as on forest floors, rock surfaces, bare soil, cracks of paved surfaces, bricks, as well as on trunks, and branches of trees.
The sexual reproduction process in bryophytes depends on availability of water, that is why their distribution is restricted to shady and moist places. Examples of bryophytes are mosses and hornworts, as shown in Figure


Activity 7
Investigating the structure of bryophytes
Materials
Mosses, hand lens, notebook, and pen or pencil
Procedure
1. Collect moss plants from the school or home environment.
2. Use a hand lens to observe the structure of a moss plant.
3. Describe the observed external features of the moss plant.
Question
What is the significance of bryophytes in ecosystems?

General characteristics of bryophytes
(a) Bryophytes live in moist, damp, and shaded areas.
(b) They do not produce flowers, fruits or seeds.
(c) They have root-like structures called rhizoids.
(d) They reproduce sexually and asexually by spores.
Distinctive features of bryophytes
(a) They are simple plants which lack true roots, stems and leaves (See Figure 5.18).
(b) They have an erect plant body, which is leafy in nature.
(c) They have no vascular tissue, meaning that they have no xylem and phloem.
(d) They usually depend on water for sexual reproduction.

Advantages of mosses
(a) They help to decompose dead logs and enhance nutrient circulation.
(b) They are early colonisers of open woodland; hence they help in creating a favourable environment for the development of higher plants.
(c) They provide food to heterotrophs, such as insects, fungi, and bacteria.
(d) They play a great role in preventing soil erosion by holding the soil particles together.
(e) They contribute in the production of oxygen to the atmosphere, which is used by animals and other organisms.
Disadvantages of mosses
(a) Moss plants are common weeds in gardens and can be difficult to eliminate.
(b) Sometimes, they grow on the surface and walls of buildings, making them look old and unattractive.

Division Filicinophyta (Pteridophyta)
Activity 8
Investigating the structure of a fern plant
Materials
Fern plants, petri dish, hand lens, notebook, and pen or pencil
Procedure
1. Collect some fern plants from the school or home environment.
Caution
Care must be taken when collecting fern plants. Get only what is required instead of destroying the whole plant.
2. Use a hand lens to examine different types of ferns.
3. Describe their external features.
4. Examine the underside of one of the fronds. Describe the structure you have observed.
Question
What is the significance of filicinophytes in ecosystems?

Members of division Filicinophyta are called filicinophytes or pteridophytes. Examples of filicinophytes are ferns, club mosses, and horsetails, as shown in Figure 5.19. Filicinophytes are much more advanced than bryophytes because they have true roots, stems and leaves.



Leaves of filicinophytes are called fronds. Fronds are usually composed of a leafy blade and petiole (leaf stalk), as shown in Figure below

General characteristics of filicinophytes
(a) They live in moist, damp and shady areas.
(b) They are less dependent on water for survival and reproduction than bryophytes.
(c) They have true roots, stems and leaves.
(d) They have vascular tissues.
(e) They reproduce by means of spores.
(f) They do not produce flowers and seeds.
Distinctive features of ferns
(a) Their leaves bear spore-producing structures called sori (singular is sorus). A sorus is a cluster of spore-producing structures called sporangia (singular is sporangium).
(b) Their leaves are arranged in a clump and are called fronds.
(c) They have a simple vascular tissue.

Advantages of ferns
(a) They constitute ground-cover in moist areas.
(b) They produce food for themselves and for heterotrophic organisms in ecosystem.
(c) They are used for decoration in homes and offices.
(d) They are the major components of coal, a fossil fuel which is made up of the remains of primitive plants.
(e) Ferns, such as Azolla sp. are used as biological organic fertiliser. They are able to fix nitrogen from the air into compounds that can be absorbed by plants.
(f) Some ferns, such as Dryopteris sp. have a medicinal value.
Disadvantage of ferns
Ferns are regarded as weeds in many places. For example, the giant fern plants are the worst aquatic weeds that threaten the life of other aquatic organisms. In terrestrial environment, some species of fern plants, such as Pteridium sp. are common weeds.
Division Coniferophyta
Activity 9
Investigating the distinctive features of conifers
Materials
A variety of conifers, such as a whole plant or branches of pine, cedar, cypress, fresh or preserved cones, notebook, and pen or pencil
Procedure
1. Collect the branches of pine, cypress, and cedar plants from the school or home environment.
Caution
Care must be taken when collecting a variety of conifer branches or cones. Get only what is required instead of destroying the whole plant.
2. Observe the structural features that are possessed by these plants which are different from those of other plants.
3. Note down the distinctive features of conifers.
Question
1. What features have you observed?
2. What features distinguish conifers from other plants?

Coniferophyta is one of the divisions of the kingdom Plantae. Plants under the division Coniferophyta are sometimes called coniferous trees or simply conifers. These conifers bear cones and they are referred to as coniferophytes.
The conifers are non-flowering plants whose seeds are not enclosed in ovaries, but are arranged spirally giving the shape of the cone. Examples of conifers include casuarinas, spruces, cedars, pines, and cypress plants. Figure 5.21 (a) and (b) shows the tree and branch of conifer.




General characteristics of conifers
Conifers possess the following features:
(a) They are non-flowering seed-bearing plants.
(b) They produce naked seeds.
(c) They have reproductive structures called cones. There are male and female cones. The male cones are smaller and usually occur in clusters. The female cones of most conifers have compound structures. See Figure 5.21 (c) and (d).
(d) They form soft wood.
(e) They have needle-like or scaled leaves with thick cuticle for protection and reduction of water loss.
(f) Conifers are widely distributed but commonly found in areas with cold climate where they form evergreen forests.

Distinctive features of conifers
(a) They bear cones.
(b) The pollen grain develops air bladder-like structure which facilitate their movement. Hence, they are wind pollinated plants.
(c) They have naked seeds, which are born in cones.
(d) The mature seeds are typically winged. This is an adaptation for seed dispersal by wind.
Advantages of conifers
(a) Conifers are the evergreen plants, which are grown in large forests and produce useful timber called softwood.
(b) Conifer forests are home to many birds and other animals.
(c) They are also used to produce wood pulp for paper making.
(d) Turpentine which is used as cleaning agent for painting as well as production of disinfectants and insecticides is also a product of conifers.
(e) Conifer trees are used as firewood; hence they are a source of heat.
(f) They are a source of food to organisms, such as insects and squirrel.
(g) Many species of Pinus are used as ornaments when planted in parks and gardens. Cypress also is commercially grown and harvested for decoration during festivals, such as Christmas.
(h) Conifers remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis.

Disadvantages of conifers
(a) Coniferous forest completely shades the ground and prevents the growth of other plants.
(b) Wood products from conifers are soft and can be easily attacked by termites if not treated.
(c) They have needle like thorny leaves that can prick and cause injury.
(d) Resins which are produced by pines catch fire easily. Thus, in case of fire outbreak in a pine forest, fire is likely to spread rapidly because of the resins.

Division Angiospermophyta
Activity 10
Investigating the structure of flowering plants
Materials
Hibiscus flower, common bean plant, maize plant, elephant grass plant, hand lens, notebook, and pen or pencil
Procedure
1. Collect hibiscus plant, common bean plants, maize plants and elephant grass plants from the school or home environment. Make sure that you carefully uproot the entire plant in order to display their root system clearly, except for hibiscus.
Caution
(a) Get only what is required instead of destroying the whole plant.
(b) Do not collect dangerous plants, such as thorny plant, itching and poisonous plants.
(c) Be careful of stinging animals, such as bees, wasps, and spider found on plants.
2. Using a hand lens, observe carefully the leaves, flower arrangement and roots of the collected plants and state the classes to which each plant belongs.
Question
Summarize the morphological differences between the classes of the collected plants in tabular form, including the characteristics, such as leaf shape, flower arrangement, and root structure.

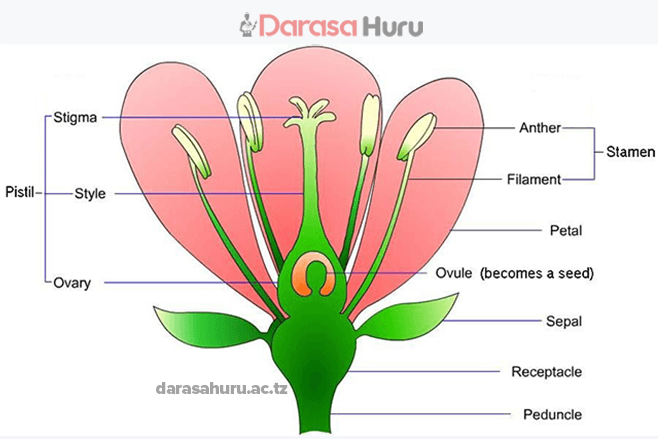
Angiospermophyta is the division in kingdom Plantae which comprises plants commonly known as flowering plants or angiosperms. Angiosperms are the most diverse and a successful group of all the plants. They are found in most habitats, such as aquatic and terrestrial habitat including deserts. They range in size from small plants, such as herbs and grasses to big trees like baobab.
General characteristics of angiosperms
The following are the general features of angiosperms.
(a) Angiosperms are found in terrestrial, freshwater and marine habitats.
(b) Angiosperms have a well-developed root system, stem and leaves.
(c) Their seeds are enclosed and protected in the ovary.
(d) They produce seed bearing fruits.
(e) They have well developed conducting tissues which contain xylem and phloem.

Classes of the division Angiospermophyta
The division Angiospermophyta is divided into two classes. These classes are Monocotyledoneae and Dicotyledoneae. The word “Mono” means one and “Di” means two. Monocots have been named from having one cotyledon and dicots from having two cotyledons. Cotyledon is the part of seed that develops into the leaves after germination.
Class Monocotyledoneae
This class contains plants with one cotyledon. Examples of plants in this class include maize, sugarcane, wheat, millet, sisal, coconuts and banana plants.

Distinctive features of the class Monocotyledoneae
(a) Flower parts normally occur in three or multiples of three. See Figure 5.22 (a).
(b) They have parallel leaf venation, as shown in Figure 5.22 (b).
(c) The embryo of monocot seeds bears one cotyledon.
(d) Monocot leaves are composed of an open or closed sheath which encloses the stem.
(e) Their vascular bundles in stems are scattered, as shown in Figure 5.23 (a).
(f) They have fibrous root system (Figure 5.23 (b)).
(g) They have long and thin leaves.


Class Dicotyledoneae
This class contains plants with two cotyledons. Examples are beans, mangoes, coffee, groundnuts and sunflower plants.
Distinctive features of the class Dicotyledoneae
(a) Floral parts are normally in four or five, or multiples of four or five. See Figure 5.24 (a).
(b) Dicot leaves have net-like venation. See Figure 5.24 (b).
(c) Their stems have vascular bundles which appear in a ring form, as shown in Figure 5.25 (a).
(d) They have tap root system, as shown in Figure 5.25 (b).
(e) Their seed embryo has two cotyledons.
(f) Dicot plants have petioles that support the leaf.
(g) They have short and broad leaves.


Advantages of angiosperms
(a) Angiosperms are important for the survival of humans and other animals. For humans, angiosperms provide foods, such as beans, rice, maize, sugarcane, and oranges. Some members of the grass family are used as food for livestock.
(b) They are habitat to many insects, birds and other animals.
(c) Different species of Angiospermatophyta are used as medicine for treating various diseases.
(d) Some angiosperms, such as cotton, flax, and hemp provide fibres that are raw materials in textile industries.
(e) Angiosperms form ground cover which prevents soil erosion.
(f) Some plants such as roses, lilies, and hibiscus make the environment attractive.
(g) They provide varieties of wood for furniture, paper, and building materials.

Disadvantages of angiosperms
(a) Some angiosperms such as thorn apple, oleander, and milkweed are poisonous. When eaten by humans and other animals as they may cause death.
(b) Drugs derived from some angiosperms can be dangerous. For example, tobacco and caffeine can be addictive.
(c) Some angiosperms, such as star grass are weed plants, which compete with food crops leading to reduction of crop yield. Others are parasites to other plant species. For example, parasitic weeds in crops, such as mango, orange and cashew nut trees, and they cause serious loss of crop yield.
(d) Some aquatic angiosperms, such as water hyacinth can colonise water bodies and affect the ecosystem as well as hindering fishing activities.