Kingdom Fungi Classes, Advantages and Disadvantages
A fungus is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms.
Task 7
Read from reliable internet sources, library and other biology books information about fungi.
The kingdom Fungi contains a variety of eukaryotic organisms that consist of bounded cell organelles, such as mitochondria and nucleus. Most of them are multicellular (made up of many cells) and some are unicellular (made up of a single cell).
Example of unicellular fungi is yeast (Saccharomyces sp.). Examples of multicellular fungi include bread mould (Rhizopus sp.), pin mould (Mucor sp.), and mushroom (Agaricus sp.).
General characteristics of Fungi
Members of the kingdom Fungi have the following general characteristics.
(a) They are found in various places including air, water, soil, food, and in the bodies of animals and plants.
(b) They are eukaryotic organisms with true nucleus which is enclosed in a nuclear membrane.
(c) They can be either unicellular, example yeast or multicellular, examples mould and mushroom.
(d) Their body is made up of a mycelium consisting of a network of fine, tube-like filaments called hyphae (except yeast).
(e) They feed saprophytically, for example mushroom; but some of them are parasitic for example Candida albicans.
(f) Some fungi form symbiotic associations with other species.
(g) They reproduce both sexually by spores and asexually by budding.
(h) They store carbohydrates in the form of glycogen.

Distinctive features of Fungi
(a) They have cell walls made up of chitin, which is a substance containing protein and complex sugars.
(b) Their bodies are made up of a mycelium consisting of a network of fine, tube-like filaments called hyphae (except yeast).
(c) They feed saprophytically, for example mushroom; but some of them are parasitic, for example Candida albicans.

Phyla of the kingdom Fungi
The members of kingdom Fungi are classified into different phyla. There are three main phyla in kingdom Fungi. These are Ascomycota, Zygomycota, and Basidiomycota.
Task 8
Search information from the library and reliable internet sources on yeast, bread mould, and mushroom. Note down their characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
Phylum Ascomycota
Members of this phylum are commonly called ascomycetes or sac fungi. This is because their sexual spores are enclosed in sac like structures known as asci (singular is ascus). Some ascomycetes such as yeast are single-celled (unicellular) organisms.

Characteristics of ascomycetes
(a) Some ascomycetes such as yeast are unicellular and others such as Penicillium sp. are multicellular.
(b) Most ascomycetes have a saprophytic mode of feeding and can grow on the surfaces of dead organic materials such as rotting fruit and other foods.
(c) They have long tube-like filaments called hyphae with cross walls.
(d) They reproduce sexually through spores known as ascospores, and asexually through fission, fragmentation, or budding

Activity 3
Investigating the structure of yeast cells
Materials
Dry yeast, water, methylene blue reagent, microscope, coverslips, microscope slides, dropper, pencil, and notebook
Procedure
1. Dissolve some dry yeast cells in water.
2. Using a dropper, place a drop of the yeast solution on a microscope slide and cover it with a coverslip.
3. Examine the specimen using the low-power objective lens of the microscope.
4. Identify some yeast cells.
5. Describe the structures you have observed in yeast cells when using the high-power objective lens of the microscope.
6. Compare your results with Figure

Phylum Zygomycota
The members of this group are known as zygomycetes because they have sexual spores known as zygospores. Zygospores are produced in the structures called zygosporangia.
They also have asexual spores known as sporangiospores, which are produced in the structures called sporangia. Zygomycetes grow as a mass of white or dark tiny threads and feed on rotting or decaying food materials like bread, cassava, pawpaw, and tomato. Examples of organisms in this group include mucor and black bread mould. See Figure.


Characteristics of zygomycetes
(a) They are multicellular.
(b) They are saprophytic, growing on decaying organic materials.
(c) They reproduce sexually through zygospores or asexually through sporangiosphores.
(d) Have hyphae without cross walls.
Activity 4
Investigating the structure of bread mould
Materials
A piece of bread, petri dish or watch glass, hand lens, forceps, microscope, microscope slides, pencil, and notebook
Procedure
1. Take a slice of bread, put it on a petri dish and moisten it.
2. Leave the bread on the moist place for 2-3 days until a greyish or dark spots appear on it.
3. Observe the changes that might have occurred on the surface of the bread
(a) Use a hand lens and observe the dark spots that have developed on the surface of the bread.
(b) Take a small sample of dark spots using forceps and place it on a microscope slide, add a drop of water, and cover with a coverslip.
(c) Put the sample on the microscope stage and observe using the low, medium, and high objective lenses.
(d) Based on your observations of the structures on the bread using the microscope, describe the features you observed. Compare your observations to the structures shown in Figure

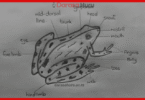
Phylum Basidiomycota
Members of the phylum Basidiomycota are called basidiomycetes. They have structures called basidia (singular is basidium) that produce sexual spores. The basidia are usually club-shaped structures.
Hence, members of this group are also known as club fungi because they all possess basidia. Their sexual spores are called basidiospores. The common examples of basidiomycetes are mushrooms and toadstools, such as Agaricus bisporus (edible mushroom).
Other examples of basidiomycetes include brackets, puffballs, and rust fungi. They are well recognisable in various habitats, especially in areas with soil rich in nutrients.

Characteristics of basidiomycetes
(a) They are multicellular organisms.
(b) They are saprophytic, growing on decaying organic matter.
(c) They reproduce both sexually and asexually.
(d) They produce sexual spores called basidiospores contained in club–like structures known as basidia.
(e) They have hyphae with cross walls (septate), volva, stipe (stem-like structure), ring, cap, and gills.
Activity 5
Investigating the structure of a mushroom
Materials
Mushroom, hand lens, scalpel, petri dish, scissors or sharp knife, pencil, and notebook
Procedure
1. Use a hand lens to examine the mushroom structure.
2. Describe the key features and structures you observe when you:
(a) view from the side; and
(b) view from the lower surface of the cap.
3. Use a scalpel or knife to cut the mushroom vertically into two equal parts.
Caution
Care should be taken when using sharp objects, such as knife.
4. Describe the features and structures you see in:
(a) the whole mushroom, as seen from the side; and
(b) cut the surface of the mushroom.
5. Compare your results with Figure 5.16.
Question
Based on your individual observations and comparisons with Figure 5.16, what conclusion can you draw regarding the structure of the mushroom?

Advantages of fungi
(a) Most strains of mushrooms and toadstools, such as Agaricus sp. Are edible. They are used as sources of food and they have a high content of proteins and vitamins.
(b) Fungi, such as yeasts (Saccharomyces sp.) are used in food manufacturing industries, such as in bakeries (they make dough to rise). Yeast is also used in brewing beer by fermenting sugars to produce alcohol.
(c) They are used in making lactic acid, citric acid, cheese, and commercial enzymes.
(d) Some fungi such as Penicillium spp. are important in production of drugs such as penicillin.
(e) Most species of fungi are used in genetic engineering and biological researches.
(f) Saprophytic fungi are very important in the decomposition of dead organisms and waste materials. Through decomposition by fungi, important nutrients are released into the soil. The nutrients are then absorbed and used by plants.
(g) Some types of ascomycetes and basidiomycetes develop symbiotic relationship with roots of higher plant to form mycorrhiza. The hyphae of fungi spread apart and increase the surface area of the vascular plant roots. This helps the plant roots to absorb more nutrients from the soil.

Disadvantages of fungi
(a) Some fungi cause diseases to human beings and other organisms. Some of the diseases caused by fungi in humans include; athlete’s foot, ringworm, meningitis, and skin infections. In some people, the fungal spores can cause allergic reactions.
(b) In plants, some fungi, such as ascomycetes cause various diseases like potato blight, maize rust, rice blast, and powdery mildew in beans and other legumes. Some fungi attack timber used in building houses and making furniture.
(c) Some fungi, such as Candida albicans live in the bodies of human beings. They grow naturally in the human body, particularly in the mouth, throat, gut, and female reproductive tracts without causing any harm. These fungi can cause infection if they grow in excess and enter deep into the body organs and systems, such as in the blood stream, kidney, heart or brain.
(d) Some parasitic fungi, such as certain types of ascomycetes produce poisonous substances called mycotoxins. The most common mycotoxin is known as aflatoxin, which is commonly found in harvested maize and groundnuts that have been left in moist places. Aflatoxin is carcinogen (cancer causing agent).
(e) Some mushrooms, such as Amanita sp. are poisonous to humans when eaten.
(f) Some fungi, such as moulds and other parasitic fungi cause food spoilage.

Advantages of Fungi
Decomposition: Fungi are essential decomposers that break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Symbiotic Relationships: Many fungi form mutualistic relationships with plants, like mycorrhizae, which help plants absorb nutrients from the soil.
Food Source: Many types of fungi, especially mushrooms and yeasts, are consumed by humans and are a source of food, protein, and nutrients.
Industrial Uses: Yeast is used to produce bread, beer, and wine. Other fungi are used in making cheese, and some fungi produce valuable compounds like vitamins and enzymes.
Medicine: Fungi are a source of important antibiotics, such as penicillin.
Bioremediation: Fungi can be used to help clean up polluted sites by breaking down certain pollutants.
Disadvantages of Fungi
Disease: Many fungi cause diseases in humans (e.g., ringworm, candidiasis), animals, and crops, leading to health problems and economic losses.
Spoilage: Fungi are a major cause of food spoilage, causing food to rot and become inedible.
Damage to Materials: They can damage materials like wood, paper, and fabric through rot and mildew.
Crop Destruction: Some fungi are plant pathogens that destroy crops, leading to significant agricultural losses.
Toxicity: Some fungi produce toxins that are dangerous to consume.
Exercise 5
1. Suppose you are in a class and your Biology teacher brings an unknown specimen. Which characteristics will you look for to confirm that it belongs to the kingdom Fungi?
2. Name the phylum to which each of the following organisms belongs.
(a) Bread mould
(b) Mushroom
(c) Yeast
3. Due to the occurrence of ringworm caused by fungi, many people view fungi as a threat. How would you educate them on the beneficial aspects of fungi in our daily lives?